
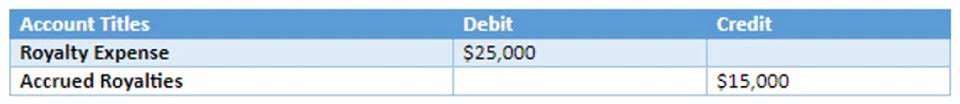
DNI is a calculation that determines the maximum income a trust undistributed profits that have accumulated in the company over time are called earnings or estate can pass through to its beneficiaries. This figure limits the trust’s distribution deduction and the income beneficiaries must report. Corporations can accumulate a certain amount of earnings without justification under the accumulated earnings credit. For personal service corporations in fields like health, law, and consulting, the credit is $150,000. Any accumulations above these thresholds must be supported by documented business needs. It is important to note that calculating E&P can be complex and requires expertise in tax regulations and accounting principles.
What Is Retained Earnings to Market Value?
Companies must adhere to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), depending on their jurisdiction. These frameworks ensure that financial statements provide a true and fair view of a company’s financial position, including its retained earnings. By examining how TechBuddy utilizes its undistributed profits, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the company’s growth prospects, financial stability, and management effectiveness. It’s important for investors and analysts to scrutinize how a company uses its undistributed profits, as it can provide insights into the company’s growth prospects and financial stability. Accumulated earnings are a vital resource for businesses, enabling growth, debt reduction, and financial stability.
Fundamentals of Undistributed Profits: Accounting Basics Quiz
These programs are designed to assist small businesses with creating financial statements, including retained earnings. We’ll explain everything you need to know about retained earnings, including how to create retained earnings statements quickly and easily with accounting software. The tax rate for the AET is 20 percent, equivalent to the top tax rate on qualified dividends. This rate is applied to “accumulated taxable income,” the portion of the current year’s retained earnings deemed excessive. However, retaining excessive income without a documented, reasonable business need can lead to scrutiny. This is to prevent using the corporate structure to shield shareholders from personal income taxes.
Accumulated Earnings vs. Dividends
- From a macroeconomic perspective, undistributed profit can contribute to economic stability by providing companies with a buffer against economic downturns.
- When a company consistently retains part of its earnings and demonstrates a history of profitability, it’s a good indicator of financial health and growth potential.
- This demonstrates the company’s commitment to long-term financial stability and growth.
- On the other hand, the stock payment transfers part of the retained earnings to common stock.
- The retained earnings are calculated by adding net income to (or subtracting net losses from) the previous term’s retained earnings and then subtracting any net dividend(s) paid to the shareholders.
- Surplus reserves and undistributed profits are both important financial tools that businesses can utilize to allocate funds for future use or retain earnings within the company.
This, of course, depends on whether the How to Invoice as a Freelancer company has been pursuing profitable growth opportunities. As the company loses liquid assets in the form of cash dividends, its asset value is reduced on the balance sheet, thereby impacting RE. Surplus reserve serves as a financial cushion for the company, providing a source of funds that can be used in times of need. By setting aside a portion of its profits as surplus reserve, a company can better weather economic downturns or unexpected expenses. Surplus reserve can also be used to fund growth initiatives, such as acquiring new assets or expanding into new markets. It reconciles the beginning balance of net income or loss for the period, subtracts dividends paid to shareholders and provides the ending balance of retained earnings.

Reducing debt levels can improve a company’s credit rating, lower interest expenses, and free up cash flow for other strategic initiatives. This is particularly beneficial in industries with high capital requirements, https://live-jimmywebstudio.pantheonsite.io/what-are-non-manufacturing-costs-or-period-costs-2/ where maintaining a strong balance sheet is crucial for securing favorable financing terms. The tax implications of undistributed earnings can be complex and multifaceted, often requiring careful consideration and strategic planning. In many jurisdictions, corporations are taxed on their earnings, and then shareholders are taxed again on any dividends they receive.
- Surplus reserve is typically created by transferring a portion of the company’s profits from the income statement to a reserve account on the balance sheet.
- Retained earnings, on the other hand, refer to the portion of a company’s net profit that hasn’t been paid out to its shareholders as dividends.
- They could use their retained earnings to cover fixed costs, invest in digital transformation, and adapt to changing market conditions.
- This means that the value of the assets of the company must rise above its liabilities before the stockholders hold positive equity value in the company.
- These undistributed profits typically accumulate in the retained earnings section of the equity portion of the balance sheet.
- To get a better understanding of what retained earnings can tell you, the following options broadly cover all possible uses that a company can make of its surplus money.
Tax Implications
In most cases in most jurisdictions no tax is payable on the accumulated earnings retained by a company. However, this creates a potential for tax avoidance, because the corporate tax rate is usually lower than the higher marginal rates for some individual taxpayers. Higher income taxpayers could “park” income inside a private company instead of being paid out as a dividend and then taxed at the individual rates. To remove this tax benefit, some jurisdictions impose an “undistributed profits tax” on retained earnings of private companies, usually at the highest individual marginal tax rate. One key attribute of surplus reserve is that it is a voluntary action taken by the company’s management. This demonstrates the company’s commitment to long-term financial stability and growth.
![]()
Both E&P and retained earnings are vital indicators of a company’s financial position and performance. They are used by investors, analysts, and tax authorities to evaluate a company’s profitability, stability, and compliance with tax regulations. Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholders, usually derived from profits, which can reduce accumulated earnings when distributed. A revenue reserve is created from the net profit generated from the company’s core operations.
- However, as the company matured, it began to face pressure from shareholders to return more of its earnings as dividends and share buybacks.
- This allows businesses to maintain control over their financial resources and pursue opportunities for expansion without relying on external financing.
- Management and shareholders may want the company to retain earnings for several different reasons.
- Dividends are payments made by a corporation to its shareholders, usually derived from profits, which can reduce accumulated earnings when distributed.
- Companies must carefully document the purpose of retained earnings to avoid penalties under AET regulations.
- This reserve is not distributed to shareholders as dividends, but is instead retained by the company for future use.
It is a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate sales and it’s reported before deducting any expenses. This reduction happens because dividends are considered a distribution of profits that no longer remain with the company. Mismanagement or ineffective use of retained earnings can hinder growth and erode investor confidence.

Accounting Basics: “Undistributed Profit” Fundamentals Quiz
While both serve similar purposes, they differ in their nature, accounting treatment, and implications for the business. In this article, we will explore the attributes of surplus reserves and undistributed profits, highlighting their similarities and differences. Companies can achieve this by reinvesting profits back into the business to fund expansion projects, research and development, or acquisitions. In scenarios where a company pays out dividends, the net income may not align with retained earnings.
